[2] Advance Docker
Before you haven't learned the Docker, please check the basic instruction first.
How to push an image to Docker Hub
Sometimes we will make a customized docker image whatever it is built from dockerfile or from a new commit. We can push to our dockerhub for sharing and reuse on different devices.
Let's go to Dockerhub and login.
If you do not have a repository for this project, let's create a new one. Click "Create Repository".
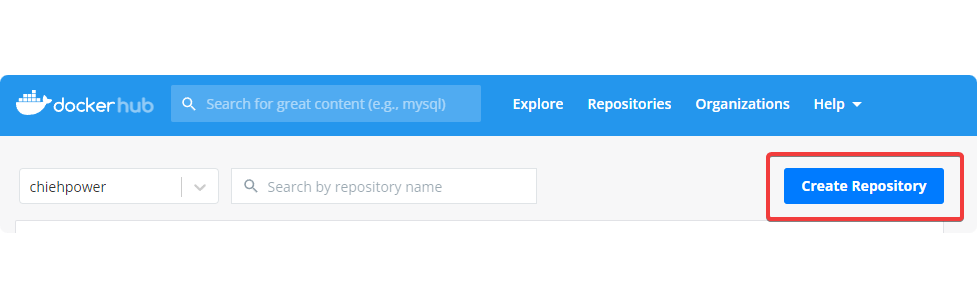
Basically you will see the similar page as below.
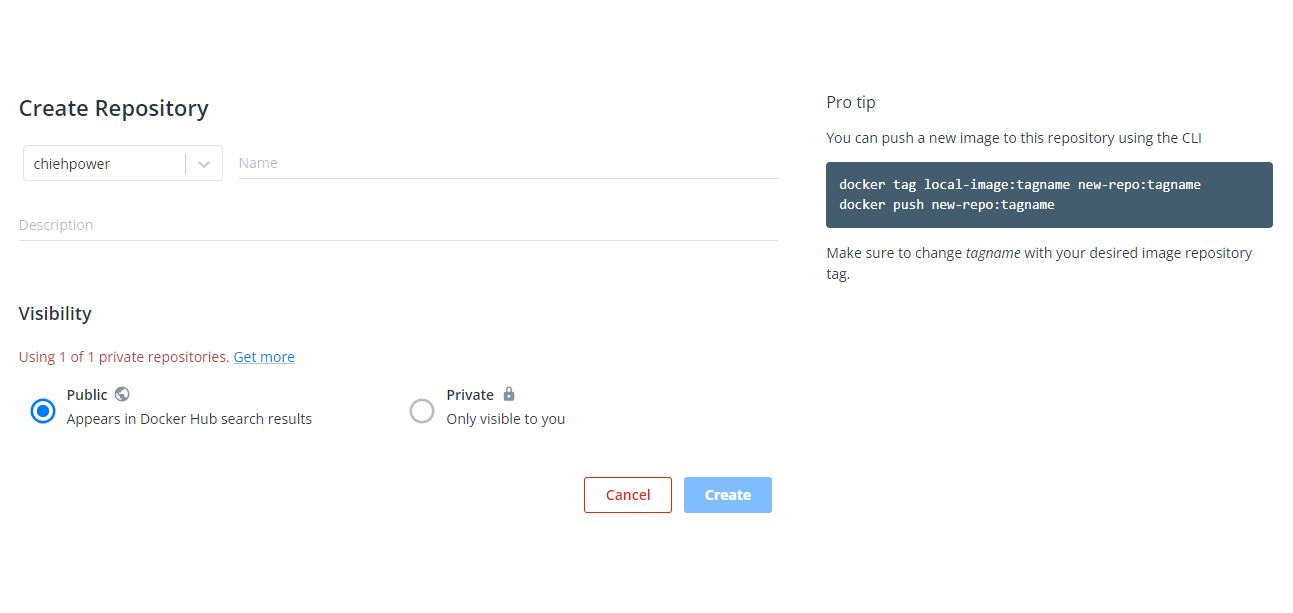
Then we can see a new repository on the dockerhub and it will show the hint to tell you how can you push an image to this repository.
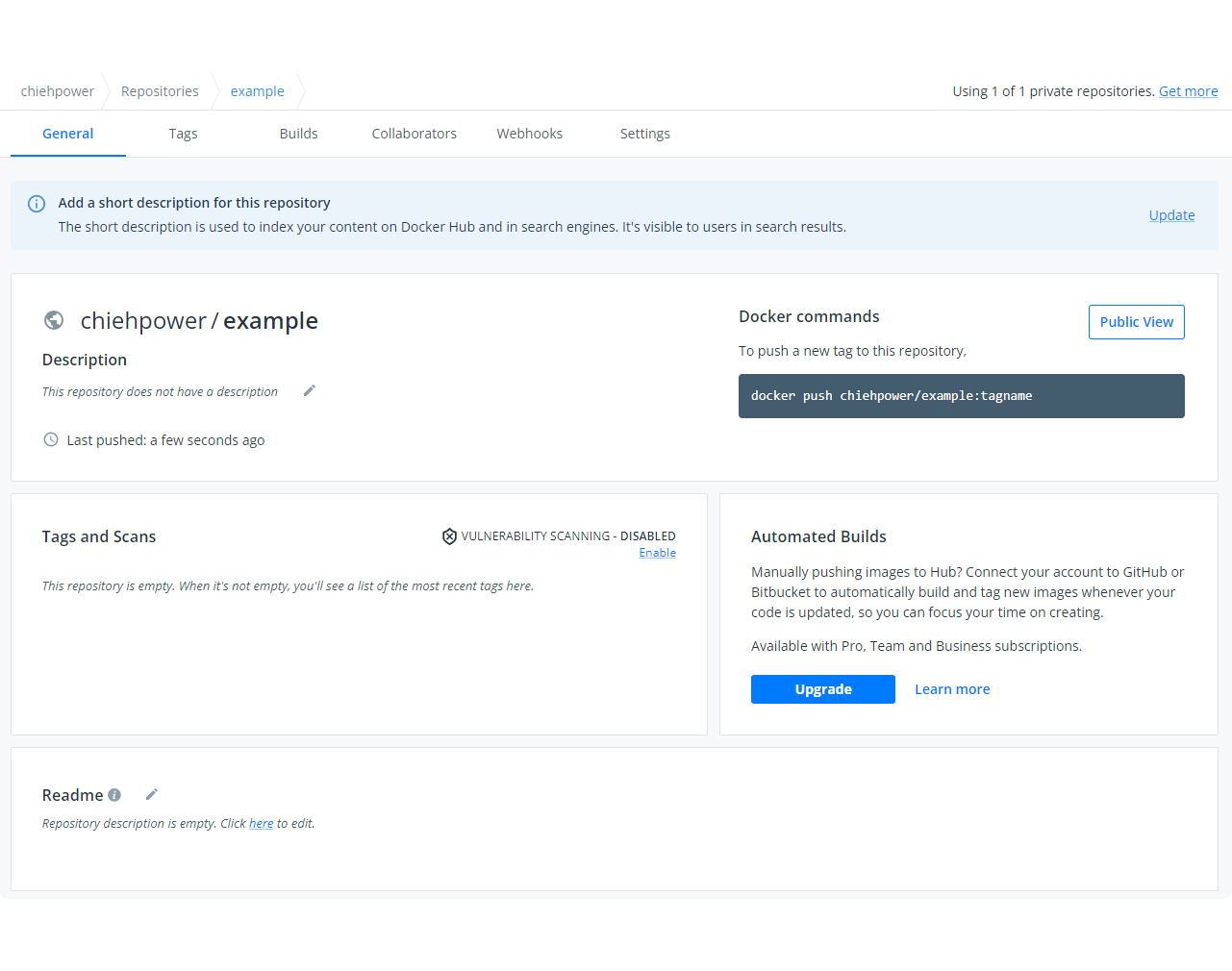
Log into the DockerHub first on our terminal.
docker login -u (your account)Change the tag of your image. We can use
docker imagesto check all images first.$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ubuntu 20.04 3bc6e9f30f51 10 days ago 72.8MBSo if I wanna push the ubuntu image to my example DockerHub repository, then I need to change the tag name.
$ docker tag ubuntu:20.04 chiehpower/example:20.04
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
chiehpower/example 20.04 3bc6e9f30f51 10 days ago 72.8MB
ubuntu 20.04 3bc6e9f30f51 10 days ago 72.8MBAnd then we can push this image to our dockerhub.
$ docker push chiehpower/example:20.04
The push refers to repository [docker.io/chiehpower/example]
c3f11d77a5de: Pushed
20.04: digest: sha256:a06ae92523384c2cd182dcfe7f8b2bf09075062e937d56537d0db0375ad221 size: 529Check the image on our repository of Dockerhub.
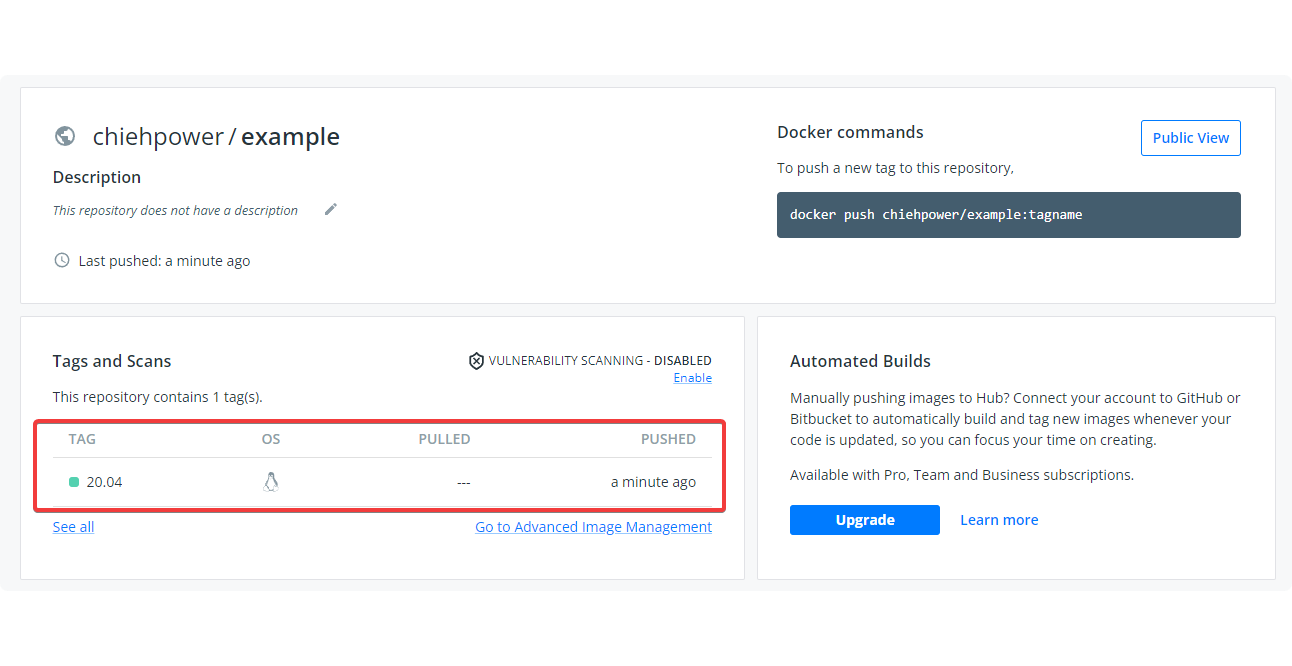
Done~
Other docker commands
docker save
Export an image to a file.
docker save (REPOSITORY):(TAG) > (File name).tar.gz
docker load
Load an image from a file.
docker load < (File name).tar.gz
docker volume
docker volume create (container name)
Reference
Clean docker image
We can use this command to clean the images that we did not use it anymore such as <images>:<None>.
docker image prune -f
However, it will not delete unless images.
Dockerfile
Please directly check my slide.
To fix the source problem:
Platform: amd64
sed -i -e 's/archive.ubuntu.com/free.nchc.org.tw/' /etc/apt/sources.list
Platform: arm
sudo sed -i'' 's/ports\.ubuntu\.com\/ubuntu-ports/free\.nchc\.org\.tw\/ubuntu-ports/' /etc/apt/sources.list
docker-compose
Resource limit
deploy:
resources:
limits:
# cpus: '0.10'
memory: 200000M
reservations:
memory: 180000M
devices:
- driver: nvidia
device_ids: ["GPU-b051e1e7-7531-b420-8827-892b063833d2"]
capabilities: [gpu]
Volume
You can set the host path for volume mounting: container path (:container) or additional access mode (host:container:ro) ro is read-only mode.
For example:
volumes:
- /var/lib/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
- /configs/mysql:/etc/configs/:ro
Achieve to docker-in-docker
docker run -ti -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock docker
"Real" docker-in-docker
docker run --privileged -d docker:dind
Storage
I changed the storing image and container location of Docker.
{
"runtimes": {
"nvidia": {
"path": "nvidia-container-runtime",
"runtimeArgs": []
}
},
"graph": "/home/user/Docker",
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"insecure-registries":["0.0.0.0:5555"]
}
We can use this command to check your all docker size.
$ sudo du -h ~/Docker --max-depth 1
4.0K /home/user/Docker/runtimes
72K /home/user/Docker/buildkit
4.0K /home/user/Docker/trust
20K /home/user/Docker/builder
20K /home/user/Docker/plugins
70G /home/user/Docker/containers
39G /home/user/Docker/volumes
53M /home/user/Docker/image
32G /home/user/Docker/overlay2
4.0K /home/user/Docker/tmp
268K /home/user/Docker/network
4.0K /home/user/Docker/swarm
140G /home/user/Docker
If you create a new container, it will accumulate the space in this /home/user/Docker/overlay2 folder.
Also, we can use this command to release useless docker image and container.
docker system prune -a
X11
If you wanna pop up a windows inside a Docker container, you need to give a env and mount the .X11-unit.
For example:
docker run -it -d --gpus all \
--privileged \
--name chieh \
--net=host \
--user=root:root \
--env=DISPLAY \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix:rw \
chieh-docker-image:latest
Also, type the command on host:
sudo xhost +